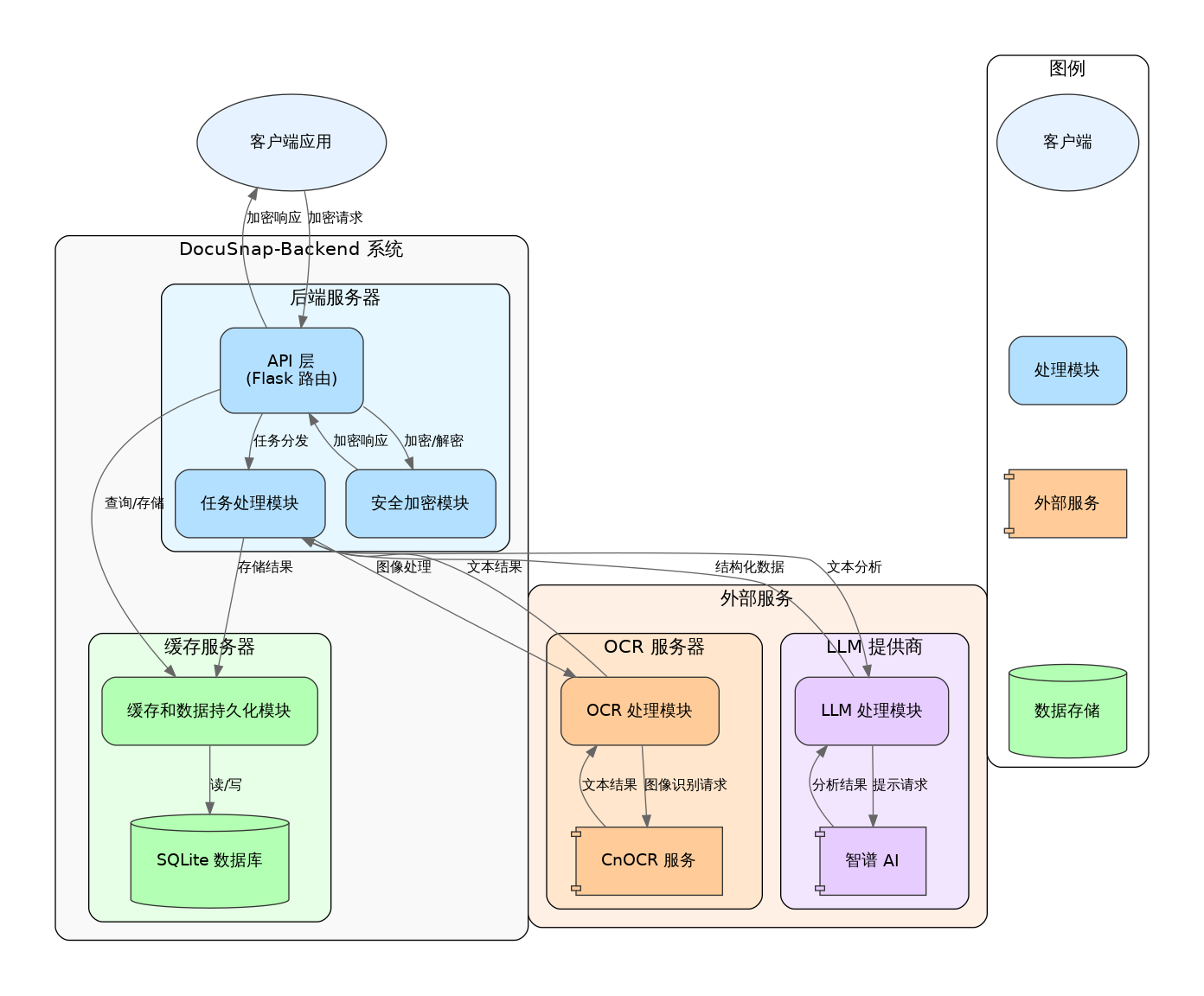
Architecture Overview
DocuSnap-Backend employs a three-layer architecture that combines layered architecture with microservice concepts, effectively breaking down system functionality into collaborating components. This page provides a high-level overview of the system architecture.
Architectural Style
The architectural style of DocuSnap-Backend can be described as:
A hybrid of layered architecture and microservices architecture
- Layered Architecture: The system internally adopts clear functional layering, including API layer, business logic layer, data access layer, etc.
- Microservice Concepts: The system treats OCR processing as an independent service, interacting via API, reflecting microservice design principles
- REST API Pattern: The system communicates with clients and external services through RESTful APIs
This hybrid architecture combines the simplicity of layered architecture with the flexibility of microservices architecture, suitable for DocuSnap-Backend’s functional requirements and scale.
System Components
DocuSnap-Backend consists of three main components:
- Backend Server:
- Core application server, based on Flask framework
- Handles client requests, coordinates task processing
- Manages task queues and worker threads
- Implements security encryption and data caching
- OCR Server:
- Independent OCR processing service
- Uses CnOCR for text recognition
- Processes image-to-text requests
- Interacts with the backend server as a microservice
- LLM Provider:
- External LLM service (Zhipu AI)
- Provides natural language processing capabilities
- Interacts with the backend server via API
- Processes text analysis and information extraction
System Architecture Diagram
The following diagram shows the overall architecture of DocuSnap-Backend:
Architectural Characteristics
DocuSnap-Backend’s architecture has the following main characteristics:
1. Separation of Concerns
- Functional Modularity: System functionality is broken down into independent modules, such as task processing, OCR processing, LLM processing, etc.
- Service Separation: OCR processing is treated as an independent service, reducing the burden on the core application
- Clear Responsibilities: Each component and module has clear responsibilities and boundaries
2. Asynchronous Processing
- Task Queue: Uses queues to store pending tasks, decoupling request reception and processing
- Worker Threads: Uses thread pools to process tasks in parallel, improving system throughput
- Non-blocking Design: Clients can query task status asynchronously, avoiding long wait times
3. Security Mechanisms
- End-to-end Encryption: Uses RSA and AES hybrid encryption to protect data transmission
- Request Validation: Uses SHA256 hash to verify the integrity of requests
- Multi-layer Security: Includes parameter validation, content validation, encryption protection, and other multi-layer security mechanisms
4. Caching Strategy
- Result Caching: Uses SQLite to store task results, avoiding repeated computation
- Status Management: Records task status, supports status queries and result retrieval
- Cache Cleanup: Regularly cleans up expired caches, optimizing storage space
5. Scalability
- Modular Design: Facilitates adding new features and extending existing ones
- Service Independence: OCR service can be scaled independently without affecting the core application
- Externalized Configuration: Key parameters are managed through configuration files, facilitating adjustment and optimization
Architecture Decisions
The following key decisions were made when designing the DocuSnap-Backend architecture:
- Choosing a Lightweight Framework:
- Using Flask rather than full-featured frameworks like Django, reducing unnecessary complexity
- Suitable for the system’s API service positioning and scale
- Adopting a Three-layer Architecture:
- Dividing the system into backend server, OCR server, and LLM provider layers
- Clear separation of responsibilities, facilitating maintenance and extension
- Asynchronous Task Processing:
- Using task queues and worker threads to handle time-consuming operations
- Improving system responsiveness and concurrent processing capability
- End-to-end Encryption:
- Implementing a complete end-to-end encryption solution to protect sensitive data
- Using RSA and AES hybrid encryption, balancing security and performance
- Using SQLite as Cache:
- Choosing lightweight SQLite as cache storage rather than complex database systems
- Suitable for the system’s caching needs and scale
These architecture decisions collectively shape the overall design of DocuSnap-Backend, enabling it to effectively meet document and form processing requirements while maintaining system simplicity, security, and scalability.